Ransomware has become an increasingly prevalent and costly threat. In 2023, ransomware attacks have shown no signs of slowing down. A report from the Malwarebytes Threat Intelligence team shows 1,900 total ransomware attacks within just four countries—the US, Germany, France, and the UK—in one year. The global cost of ransomware is expected to exceed $30 billion in 2023. The average ransom payment has exceeded $100,000, with the average demand being $1.5 million.
Despite the increasing threat, many organizations believe they are prepared to thwart a breach. However, half of the organizations surveyed still fell victim to ransomware last year. This highlights the importance of understanding ransomware and implementing effective prevention strategies.
This article will guide you on how to prevent ransomware attacks in 2023. We will explore good cyber hygiene practices, network security measures, backup strategies, and more. Our goal is to equip you with the knowledge and tools to safeguard your data against this growing cyber threat.
What is Ransomware, and How Does it Work?
Ransomware is a type of malicious software or malware that threatens a victim by destroying or blocking access to critical data or systems until a ransom is paid. It’s a form of malware that locks the user out of their files or their device and then demands payment to restore access.
Ransomware attacks typically start with a breach of your computer or network. Often, this breach is enabled by a successful phishing attack. For example, you might click on a suspicious link in an email that downloads ransomware onto your computer or gives an attacker access to your device. Once an attacker is inside your computer, it can take as little as a few hours for them to deploy ransomware. The malware will automatically encrypt all of the files on your computer, effectively locking you out of your device.
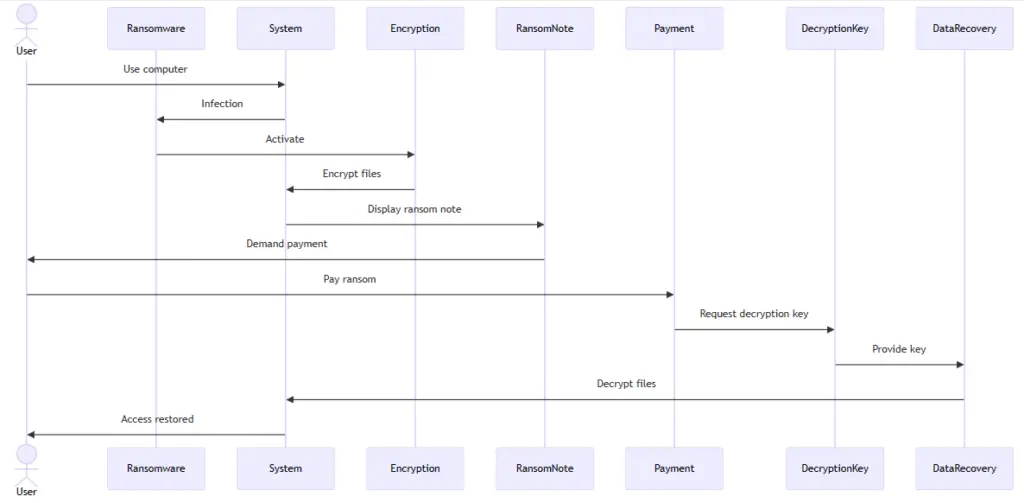
In a typical ransomware attack, the hacker will offer to decrypt your files for a price. This is the ransom in the attack, and it can range from hundreds of dollars for an individual to millions for a large corporation. Some ransomware will delete your files after a specific, predetermined amount of time passes, which puts pressure on victims to pay up quickly. In other ransomware attacks, the attacker will also steal copies of your data and threaten to release them if you refuse to pay.
What are the Types of Ransomware?

Ransomware can be classified into different types based on how it encrypts files, how it is delivered, and what it targets.
Based on encryption
- Crypto ransomware: This is a prevalent form of ransomware that encrypts the victim’s files using complex cryptographic algorithms, rendering them inaccessible. The attacker then demands a ransom, typically in the form of cryptocurrency, in exchange for the decryption key.
- Locker ransomware: Unlike crypto-ransomware, locker ransomware does not encrypt files. Instead, it locks the victim out of their device or system, often by changing the login password or encrypting the boot sector.
- Scareware: Scareware is a type of malware designed to scare victims into paying a ransom. It often displays fake messages claiming that the victim’s computer has been infected with a virus or that their files have been encrypted. However, scareware does not actually encrypt or lock files.
Based on delivery
- Email ransomware: This type of ransomware is delivered via email attachments or links. When the victim clicks on the link or opens the attachment, the ransomware is downloaded and installed on their computer.
- Web-based ransomware: This type of ransomware is delivered through malicious websites. When the victim visits the website, the ransomware is downloaded and installed on their computer without their knowledge.
- Exploit kit ransomware: This type of ransomware exploits vulnerabilities in software to infect computers. Exploit kits are often used to deliver ransomware to businesses and organizations.
Based on target
- File-encrypting ransomware: This encrypts the files of the victim, rendering them inaccessible. Once the files are encrypted, a ransom demand is made for the decryption key.
- System-encrypting ransomware: This type of ransomware encrypts the victim’s system, making it unusable.
- Database-encrypting ransomware: This type of ransomware encrypts the victim’s database, making it inaccessible.
Other types
- Ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS): RaaS is a business model where ransomware developers sell their ransomware kits to criminals. This makes it easier for criminals to launch ransomware attacks, even if they do not have technical expertise.
- Double extortion ransomware: Double extortion ransomware is a sophisticated cyberattack tactic where attackers not only encrypt the victim’s data, making it inaccessible, but also threaten to leak or sell the stolen data if the ransom isn’t paid.
- Supply chain ransomware attacks: Supply chain ransomware attacks target software vendors or suppliers to gain access to their customers.
Best Practices to Prevent Ransomware Attacks
Ensure Email Security
Identify and Report Email Phishing Expeditions
Phishing expeditions are a common method used by cybercriminals to trick recipients into divulging sensitive information or downloading malware. It is estimated that 90% of successful cyber attacks start with email phishing. Therefore, it is crucial to identify and report these expeditions to prevent falling victim to these attacks.
Phishing emails often use deceptive links as the primary tactic. Attackers evolve their methods to trick users into clicking these links. They also use identity deception, which takes multiple forms, including business email compromise (BEC) and brand impersonation. These deceptive emails can easily bypass email authentication standards.
If you receive a phishing email, you should forward it to the Anti-Phishing Working Group at reportphishing@apwg.org. If you receive a phishing text message, forward it to SPAM (7726). You should also report the phishing attempt to the Federal Trade Commission at ReportFraud.ftc.gov
Conduct Malicious Email Recognition Drills
Email is one of the most common vectors for ransomware attacks. Therefore, conducting malicious email recognition drills is a crucial part of any cybersecurity training program.
These drills should aim to teach employees how to spot phishing emails, which are often used in ransomware attacks. They should cover common signs of phishing emails, such as suspicious sender addresses, generic greetings, spelling and grammar mistakes, and requests for personal information.
To conduct effective malicious email recognition drills:
- Regular Quizzes: Regular quizzes on phishing can help employees recognize that they are not as informed as they thought, making them more receptive to training.
- Real-World Examples: Use real-world examples of phishing emails in your drills to make the training more relevant.
- Immediate Feedback: Provide immediate feedback during the drills so that employees can learn from their mistakes in real-time.
- Repeat Offenders: Have a plan in place for dealing with individuals who repeatedly fail phishing simulations.
Upgrade Your Email Security Infrastructure
Some of the most important email security best practices include employee training and awareness, anti-spam and anti-phishing filters, email authentication security protocols, multi-factor authentication (MFA), secure email gateway (SEG), email encryption, monitoring and logging email activity, and implementing email security policies.
Advanced detection techniques such as structural analysis of headers, body copy, images, links, attachments, and payloads using heuristics and machine learning models specifically designed for phishing signals can be used. Sentiment analysis can detect changes in patterns and behaviors (e.g., writing patterns and expressions).
Schedule Regular Data Backups
Data losses can take many forms, ranging from hard drive failures to ransomware attacks or even human error or physical theft. Regardless of what causes the data loss, the user can always restore their computer from backup files.
To ensure that you have a recent copy of your data in case of a ransomware attack or other data loss event, it is important to back up your data regularly. Depending on the size of the data you want to protect and the frequency of backups, you can choose from three backup options:
- Full backups: This method backs up every file on your device.
- Differential backups: This method only backs up files that have been added or changed since the last full backup.
- Incremental backups: Like a differential backup, incremental backups also only back up data that has been changed or added since the last backup.
There are several ways to schedule regular data backups. For instance, if you’re using cPanel, you can set your scheduling and retention preferences in WHM. If you’re using SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), you can create a maintenance plan.
Establish Offline, Immutable Backup Systems
Immutable backup prevents scenarios like ransomware attacks by saving a version that cannot be altered, deleted, or overwritten, regardless of the circumstance or threat actor; this allows you to recover your data without paying a ransom.
The data stored in an immutable backup solution is tamper-proof; this means it cannot be modified, deleted, or overwritten. In immutable backup, data is stored in a read-only format, prohibiting write privileges to ensure data cannot be changed.
Activate Firewalls for Ransomware Detection
Firewalls act as a barrier between your trusted internal network and untrusted external networks, such as the Internet. They can block certain types of traffic based on the access controls set by the organization. They can also prevent unauthorized access to or from a private network. Firewalls provide an additional layer of security that has its own access point, login credentials, and protection.
To activate firewalls for ransomware detection, you should not allow uninspected traffic through. Reduce the attack surface by blocking unknown files unless they enter from a very trusted party. Keep a log on this for retrospective analysis. Decrypt all traffic in order to detect files and, specifically, malware, including ransomware.
Implement Network Segmentation Strategies
Network segmentation is a network security practice and defense-in-depth strategy of dividing the main network into multiple, smaller subnetworks to protect sensitive data better and limit lateral movement to the rest of the network.
Network segmentation can limit the scope of an attack, prevent malware from spreading, and disrupt lateral movements across your IT ecosystem. Each individual subnetwork or “zone” represents an additional layer of security that has its own access point, login credentials, and firewall protection.
There are three main ways to segment a network: VLAN segmentation, firewall segmentation, and SDN segmentation.
- VLAN (Virtual Local Area Networks) Segmentation: Most segmented networks use VLANs to create smaller groups of subnetworks or subnets that are connected virtually in the same broadcast domain.
- Firewall Segmentation: Organizations can set up firewalls between each application layer to protect each internal zone of a network.
- SDN (Software-Defined Networking) Segmentation: SDN allows network administrators to manage network services through the abstraction of lower-level functionality into virtual services.
Disable Risky Macro Scripts in Documents
Macro scripts in documents, especially those downloaded from the internet, can pose a significant security risk. They are a common way for malicious actors to gain access and deploy malware and ransomware. Disable risky macro scripts in documents to improve the security of applications. When users open a file that came from the internet, such as an email attachment, and that file contains macros, a warning message will be displayed. This change helps prevent users from inadvertently opening files from the internet that contain macros.
Strengthen Endpoints Against Potential Attacks
Endpoint attacks have evolved into a critical concern, posing substantial threats to businesses across all industry verticals. To effectively prevent ransomware attacks, it’s crucial to secure all endpoints, including mobiles, PCs, and IoT devices, especially as the number of endpoints and the prevalence of remote work continue to grow. This security encompasses implementing robust measures like firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), anti-virus software, data encryption, and advanced, automated endpoint protection. Additionally, enforcing the Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) Policy, taking extra precautions during travel, and properly wiping devices before selling or disposing of them are essential practices.
The escalation of endpoint attacks poses significant threats to businesses in various industries, with the expanding attack surface making organizations increasingly vulnerable. The initial step in endpoint security involves cataloging and assessing vulnerabilities to control network access and focus on the most risky and sensitive endpoints. Furthermore, deploying data loss prevention (DLP) solutions can fortify endpoints against attacks by preventing unauthorized access to sensitive data and ensuring that sensitive information doesn’t leave the corporate network.
Deploy Advanced Antivirus and Anti-malware Solutions
Endpoint protection platforms (EPPs) provide the facility to deploy agents or sensors to secure managed endpoints, including desktop PCs, laptop PCs, servers, and mobile devices. EPPs are designed to prevent a range of known and unknown malicious attacks.
There are several leading antivirus software solutions available in the market. These include Bitdefender GravityZone, Sophos, Trend Micro, Malwarebytes, and Microsoft Defender for Endpoint.
Promote Security Awareness Training and Workshops
Cybersecurity awareness workshops are an essential tool in the fight against ransomware infection. These workshops aim to educate employees about the various types of cyber threats, including ransomware, and how to prevent them.
Workshops should cover a broad range of topics, including the importance of cybersecurity both personally and organizationally, how to recognize phishing attacks, safe downloading and installation practices, recognizing suspicious executable files and links, keeping systems up to date, and verifying software and website legitimacy.
To promote these workshops effectively within an organization:
- Get Employees On Board: Start by ensuring that all employees understand the importance of these workshops and are willing to participate.
- Endorse the Training Across Your Organization: Make sure that the training is endorsed at all levels of the organization, from top management down.
- Make it Interactive: Interactive sessions are more engaging and help to ensure that the information is absorbed.
- Keep it Simple and Provide Relevant Content: The content should be easy to understand and directly relevant to the employees’ roles.
Adopt Zero Trust Architectural Principles
The Zero Trust model is a security concept centered on the belief that organizations should not automatically trust anything inside or outside its perimeters and instead must verify anything and everything trying to connect to its systems before granting access. Here are some key principles:
- Assume the network is always hostile: Both external and internal threats are always present on the network.
- Authenticate and authorize every device, user, and network flow: Every request is fully authenticated, authorized, and encrypted before granting access.
- Know your architecture: This includes users, devices, services, and data.
- Assess user behavior, service, and device health: Constant assessment can help detect anomalies that may indicate a security issue.
Limit Access to Virtualization Management Tools
Virtualization management tools are essential for managing virtual environments. However, they can also be a potential entry point for cyber threats. In 2023, limiting access to these tools has become a standard practice in cybersecurity.
Here are some strategies to limit access:
- Implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): RBAC ensures that only authorized individuals have access to virtualization management tools.
- Regularly update and patch virtualization software: This helps protect against known vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit.
- Monitor and log activity: Keeping a record of all activities can help detect any unauthorized access attempts.
Integrate SIEM Systems for Real-time Analysis
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools play a crucial role in an organization’s security operations, allowing security teams to monitor, detect, and respond to security incidents more efficiently and effectively. SIEM tools provide real-time analysis of security alerts generated by applications and network hardware. Here are some key features of SIEM systems:
- Real-time analysis: SIEM tools use real-time analytics to detect and prioritize events or activities that may represent a threat.
- Log management: They offer a wide range of log management features.
- Automated security scanning: This includes activity analytical tools and compliance auditing facilities.
Subscribe to Threat Intelligence Services for Updates
Threat Intelligence Platforms (TIPs) process external threat feeds and internal log files to create a prioritized and contextualized feed of alerts for a security team. TIPs also enhance security tools with consolidated and improved threat feeds. Here are some top Threat Intelligence Platforms:
- Anomali ThreatStream
- IBM X-Force Exchange
- IntSights Threat Intelligence Platform
- LookingGlass Cyber Solutions
- Recorded Future
- SolarWinds Security Event Manager
- ThreatConnect
Perform Regular Security Audits and Assessments
Performing regular security audits and assessments is a significant first step before implementing a risk-prevention plan. Here are some strategies for performing security audits:
- Use an industry-standard benchmark: Evaluate your organization’s current security posture.
- Automated IT security audits: Also known as vulnerability assessments, while procedural issues are dealt with by risk management.
- External audits: Involve independent entities evaluating your security posture.
- Internal audits: Conducted by individuals within the organization.
Stay Updated: Regular Software Patching
Ransomware attacks often exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software or operating systems. A vulnerability is a software flaw that can be used for malicious purposes. As these vulnerabilities are discovered, software vendors regularly issue fixes for them in the form of software updates. Not updating your programs and operating system regularly is akin to leaving your house’s front door unlocked, allowing ransomware attackers easy access.
Ensure All Software Downloads are from Trusted Vendors
The internet is a vast marketplace for software, with countless vendors offering their products. However, not all vendors are trustworthy, and downloading software from unknown sources can expose your systems to various risks.
Apps from unknown sources may not have been adequately tested for security vulnerabilities. This means they might contain malware or other harmful software that could damage your device or steal your data. Cybercriminals often use these platforms to distribute ransomware and other malicious programs.
When you download software, ensure it’s from a trusted vendor. Trusted sources have strict regulations for app developers and examine each app before making it available for download. This helps ensure the apps are secure and free of any malicious code.
Enforce Strict Password and Authentication Policies
Password security is a critical line of defense against ransomware threats. A strong and secure password can significantly reduce the risk of cybercriminals guessing your password and accessing sensitive data. In fact, compromised passwords were responsible for 80% of all data breaches in 2019, leading to financial losses for both businesses and consumers.
Enforcing strict password and authentication policies is a key strategy in preventing ransomware attacks. This includes implementing policies such as mandatory password changes at regular intervals, prohibiting the reuse of old passwords, and requiring complex passwords that include a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Systems
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is another effective method for preventing ransomware attacks. MFA requires users to provide proof from two or more authentication factors before access is granted. Even if ransomware hackers manage to steal a password, gaining access to a second authentication factor is much more challenging and requires significantly more effort.
Implementing MFA or Two Factor Authentication (2FA) can help protect remote network and email access as well as administrative access. This prevents system intruders from breaching networks to deploy ransomware, erase valuable data, or steal sensitive information for malicious purposes through a variety of commonly successful cyberattacks such as phishing or keylogging.
Fortify Internet-facing Applications: Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP)
The Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is a popular tool used to connect to office computers remotely. However, it has become a hot target for ransomware attacks due to its long history of vulnerabilities and often reckless use. In fact, RDP accounts for 70%-80% of the attack vectors leveraged to deliver ransomware.
RDP uses port 3389 as its default listening port. Attackers are aware of this and can run a script to scan for 3389 ports that have been left open to the internet. Once an exposed port is found, the threat actor has to get ahold of the login credentials. They can do this through any of the typical methods of obtaining credentials, such as social engineering or often brute force attacks.
The best way to ensure your organization is not the victim of an RDP attack is to make sure your RDP ports are not left open to the internet. Often, this is accomplished by the use of a virtual private network (VPN), which acts as an encrypted tunnel to provide secure access.
Additionally, Not every device in your network may need RDP access. Ensuring RDP access is turned off and blocked for those who don’t need it will limit your exposure. You can also use an allow-list only to allow approved IP addresses to connect to the RDP server.
Draft and Test an Incident Response Plan
An incident response plan is crucial in preparing for and recovering from ransomware attacks. The plan should include detailed step-by-step instructions on how to respond to different types of ransomware attacks, as well as contact information for key personnel who will be responsible for managing the response.
Bottom Line
Ransomware attacks have become more sophisticated and prevalent in 2023, posing a serious threat to individuals, businesses, and governments. To prevent ransomware attacks, it is essential to adopt a comprehensive and proactive approach that covers email security, data backup, network segmentation, endpoint protection, security awareness, software patching, authentication policies, and incident response. By following the advanced threat protection practices outlined in this article, you can reduce the risk of falling victim to ransomware and mitigate its impact if it happens.



How to Prevent Ransomware Attacks: Expert Tips and Practices (2023)