WordPress is the undisputed king of content management systems, powering over 40% of all websites worldwide. But the same simplicity that makes it so appealing can also make it vulnerable to security breaches. Unfortunately, even the slightest WordPress security mistake can lead to devastating consequences. As a WordPress site owner, it’s crucial to avoid common WordPress security mistakes to keep your site safe from the ever-increasing number of cyber threats.
Outdated Operating System or Server Software
One of the most common causes of website hacks is an outdated operating system or server software. Hackers often take advantage of vulnerabilities in outdated software to gain unauthorized access to WordPress sites, steal sensitive information, or spread malicious software, resulting in data theft, loss of revenue, and damage to your reputation. In fact, according to a report by RiskBased Security, it saw a 141% increase in the number of records exposed in data breaches.
To protect your WordPress website, you must keep your operating system and server software updated. By doing so, you ensure that your website is running on the latest and most secure WordPress version, which reduces the risk of a security breach.
How to Update Your Operating System and Server Software?
Updating your operating system and server software is a straightforward process. Most operating systems and server software have an auto-update feature that automatically downloads and installs the latest security patches and updates. However, if you prefer to update manually, you can do so by following these steps:
1. Check for updates
Check if there are any available updates for your operating system or server software. Most updates can be found in the “Updates” section of your system settings.
CentOS / AlmaLinux / Fedora / Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL)
If you are running any flavor of CentOS, AlmaLinux, Fedora, or RHEL, you can use yum:
yum check
Yum check will check your system for available updates. When you are ready to perform those updates, you can run the following command:
yum update
Ubuntu
On Ubuntu, you can perform the following command to see what packages are available for upgrades:
apt list --upgradable
In order to apply the updates, perform the following command on Ubuntu:
sudo apt-get upgrade
2. Download updates
Download and install the updates as soon as they become available. This will ensure that your system is running on the latest and most secure version.
3. Restart your server
After installing updates (and especially after any kernel update), it is recommended that you restart your server to ensure that all updates are properly applied and take effect. With most Linux operating systems, you can reboot the server with a simple reboot command.
Outdated PHP Versions
PHP is a scripting language used to build dynamic websites. It is a popular choice among web developers because it is free, easy to use, and can run on multiple platforms. PHP powers many websites, including those hosted on the WordPress platform. However, using outdated versions of PHP can pose a severe security risk to your WordPress site. According to a study by Sucuri, over 60% of hacked WordPress sites were using an outdated version of PHP.
Hackers often target websites running on outdated PHP versions because they have known vulnerabilities that can be easily exploited. Keeping your PHP version updated is crucial to maintaining website security.
How to Update Your PHP Version?
To update your PHP version, you should contact your web hosting provider and ask them to upgrade your server’s PHP version to the latest stable release. Alternatively, you can update PHP yourself if you have access to your server’s control panel.
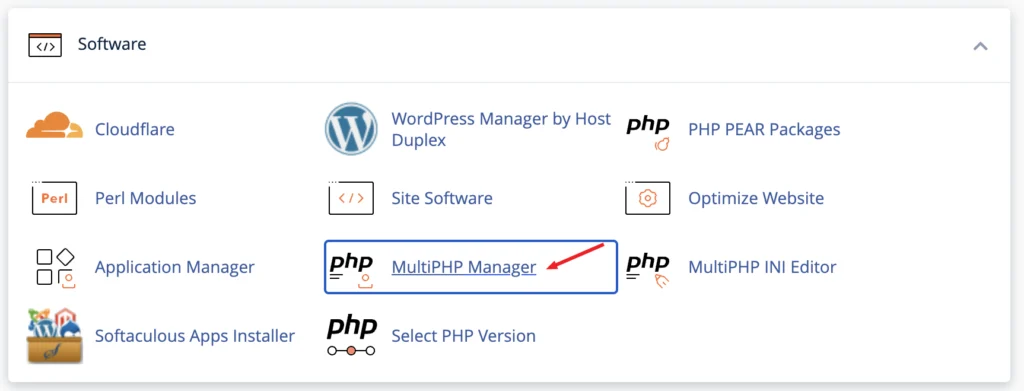
Update the PHP version in cPanel
- Log into your cPanel and select the MultiPHP Manager
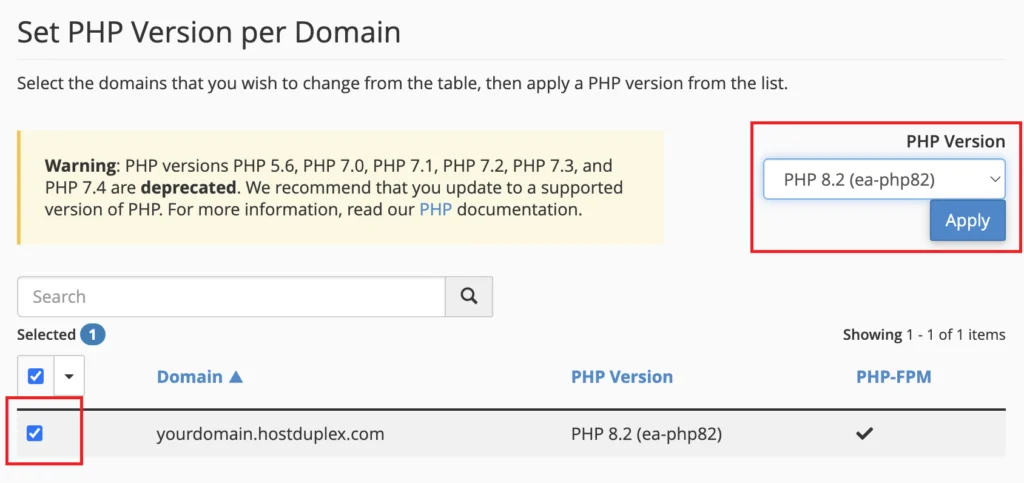
- Select your domain, PHP version of your choice, and click Apply
Outdated themes and plugins
A recent study found that 6 out of 18 components are outdated on a single WordPress site. With every additional WordPress plugin installed on the website, the risk of being exposed to a potential vulnerability increases. The fact that WordPress sites are lagging behind with updates increases the risk even more. Jeff Mains, CEO of Championship Leadership Group, told Host Duplex, “Once sites are infected with malware, it can spread to other parts of a server, damaging other sites hosted on the same server.”
Like any software, WordPress requires regular updates to maintain optimal performance and security. Failure to update your WordPress core, plugins, and themes can lead to security vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit.
Outdated plugins and themes often contain known security vulnerabilities, which can be exploited by malicious actors.
Harman Singh, Director at Cyphere
Also read, 10 Must Have WordPress Plugins for Optimal Performance in 2023
How to Keep Your WordPress Core, Plugins, and Themes Up-to-date?
To keep your WordPress plugins, themes, and WordPress core up-to-date, you should regularly check for updates and install them as soon as possible. You can also enable automatic updates for your WordPress core and plugins, which can save you time and ensure that your site is always running on the latest version.
It is also recommended to remove unused themes or plugins. This helps to minimize the risk of vulnerable WordPress plugins being exploited by hackers.
To remove unused Plugins, Go to the ‘Plugins’ section of your WordPress dashboard and click on ‘Installed Plugins’.
- Look for any inactive plugins and select them all.
- From the dropdown menu, click on ‘Delete’ to remove them.
Similarly, to delete any unused WordPress themes, go to the ‘Appearance’ section and click on ‘Themes’.
- Select the theme you want to remove.
- Click on the ‘Delete’ button located in the bottom right-hand corner of the screen.
Using Third-party Plugins Only from Trusted Authors/Sources

Third-party plugins are a great way to add additional functionality to your WordPress website. However, using plugins from untrusted authors or sources can contain malicious code that can pose a significant security risk. In fact, according to a report by iThemes, over 97% of WordPress vulnerabilities were caused by third-party plugins.
Why Choose Trusted Authors and Sources for Third-party Plugins and WordPress security plugins?
Using plugins from trusted authors and sources reduces the risk of installing malicious code on your WordPress site. Trusted authors and sources usually have a track record of producing high-quality WordPress plugins that are regularly updated to address known vulnerabilities.
The best way to protect yourself is to use the right tools to keep your site secure, and have regular backups in place.
Michael Miller, CEO of VPNOnline.com
How to Choose Trusted Authors and Sources for Third-party Plugins?
When choosing a third-party plugin, it’s important to do your research to avoid WordPress security mistakes. Here are some tips for choosing trusted authors and sources:
1. Check plugin reviews
Check the plugin’s reviews to see what other users are saying about it. Look for plugins with high ratings and positive reviews.
2. Check the author’s reputation
Check the author’s reputation by searching for their name on Google or reading their website’s “About” section. Look for authors who have a good reputation in the WordPress community.
3. Check plugin updates
Check the plugin’s update frequency to ensure that it is regularly updated. Plugins that are not updated regularly are more likely to contain vulnerabilities.
4. Check the plugin’s code
Check the plugin’s code for any suspicious or malicious code that could pose a security risk. You can check PHP code for vulnerabilities using tools like ChatGPT or Synk.io’s PHP code checker.
Top WordPress Security Tools and Plugins
Some of the most popular WordPress tools and plugins that can help in avoiding WordPress security mistakes are:
Wordfence
Wordfence offers a complete security solution for WordPress, including malware scanning, firewall protection, and login security features.
Sucuri
Sucuri is a cloud-based security platform that provides website scanning, malware removal, and website firewall protection for WordPress sites.
iThemes Security
iThemes Security is a powerful security plugin with features like malware scanning, brute force protection, and two-factor authentication for enhanced WordPress security.
WPScan
WPScan is a dedicated vulnerability scanner that checks WordPress websites for known security vulnerabilities, helping you identify and fix potential issues.
Lack of Backups
Not backing up WordPress sites is one of the most common WordPress security mistakes. Backups are copies of your website’s files and database that can be used to restore your website in case of a security breach or other issues.
Many hosting providers offer automatic backup solutions, making it easier for WordPress users to keep their websites protected. Additionally, you can leverage WordPress backup plugins to ensure seamless data preservation, effortless site migration, and swift disaster recovery for your website.
Failing to back up your website can have devastating consequences in the event of a security breach or data loss. Many people make the mistake of backing up their website to the same server, which can be problematic if the server fails. Both on-site and off-site backups are recommended.
Why is Having Regular Backups Essential for Your Website?
Regular backups are critical for maintaining the integrity and availability of your website’s data. Without backups, you risk losing all your data in case of a security breach, server failure, or human error. According to a report by Cybersecurity Ventures, ransomware attacks are predicted to cost businesses over $265 billion by 2031.
Regular backups ensure that you always have a recent copy of your website’s files and database. In case of a security breach, you can quickly restore your website to its previous state using a backup. Regular backups also protect your website from data loss caused by hardware failures or human errors.
How to Back up Your Website?
There are several ways to back up your website. Here are some common methods:
1. Use a backup plugin
Automate the backup process with popular plugins like UpdraftPlus, BackupBuddy, and VaultPress.
2. Use your hosting provider’s backup service
Check if your hosting provider offers backups and how to access them.
3. Manually backup your website
Use an FTP client to download your website’s files and a database management tool to export your website’s database.
Weak Passwords

Passwords are one of the most critical aspects of securing your WordPress site. Weak passwords can easily be hacked, compromising the security of your website. Hackers often use brute force attacks to gain access to WordPress user accounts by guessing passwords through repeated login attempts. According to a study by Nord, the most commonly used passwords in 2021 were “123456” and “password“.
In another study, it was revealed that hackers attempt to guess passwords at an alarming rate of one attack every 39 seconds. This highlights the need to use strong and unique passwords for your WordPress site.
How to Create a Strong Password for Your WordPress Site?
Creating a strong password can be quite easy. Here are some tips to follow when creating a password for your WordPress site:
- Use a combination of upper and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Make your password at least 12 characters long.
- Avoid using common words, phrases, or personal information that can be easily guessed.
- Use password policy plugins or password managers to generate and store unique passwords for each of your accounts.
How to Manage Your WordPress Passwords?
As your website grows, managing your passwords becomes more important. Here are some best practices to follow when managing your WordPress passwords:
- Change your passwords regularly.
- Use a different password for each of your accounts.
- Avoid writing your passwords down or storing them in an insecure location.
- Using a password manager can help you generate and store strong, unique passwords for each WordPress account.
Ignoring User Roles/Permissions

User roles and permissions are essential for controlling access to your website’s backend. Many WordPress site owners make the mistake of giving users more permissions than necessary, which can lead to accidental or intentional changes that compromise site security.
Neglecting to audit your user roles and permissions can result in unauthorized access, data theft, and other security breaches. By assigning the correct user roles and permissions, you can limit access to sensitive areas of your site and prevent unauthorized access.
Why Regularly Auditing User Roles and Permissions Is Important?
Auditing your user roles and permissions regularly is crucial for maintaining the security of your WordPress site. By doing so, you can:
- Ensure that only authorized users have access to sensitive areas of your site.
- Remove any unused or unnecessary user accounts.
- Identify any potential security risks or vulnerabilities.
How to Audit Your User Roles and Permissions?
To audit your user roles and permissions, follow these steps:
- Review your user roles and permissions regularly.
- Remove any unused or unnecessary user accounts.
- Ensure that each user has the appropriate level of access based on their role.
- Use WordPress security plugins like User Role Editor to customize user roles and permissions.
Neglecting File Permissions

File permissions are an often-overlooked aspect of WordPress security. File permissions determine who can read, write, and execute files on your website’s server. If not configured correctly, they can expose your site to potential security risks. A report by Sucuri found that improper file permissions are a significant factor contributing to the vulnerability of WordPress sites.
Why do Proper File Permissions Matter for Your Website’s Security?
Proper file permissions ensure that only authorized users can access and modify files on your website. Improper file permissions can lead to unauthorized access or modifications, which can compromise the security of your site.
How to Set Proper File Permissions for Your WordPress Site?
To set proper file permissions for your WordPress site, follow these steps:
- Avoid giving write permissions to directories or files unless necessary.
- Set the file permissions to 644 for all files and 755 for all directories.
- Avoid setting file permissions to 777, as this grants full access to all users.
This ensures that directories are readable and executable and files are readable but not writable.
Not Using 2FA

According to a report by Google, 2FA can prevent 99% of automated attacks. Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a security feature that requires two forms of authentication before granting access to an account. This adds an additional layer of security that can protect your WordPress site from unauthorized access. By requiring a second form of authentication, such as a code generated by an app or sent to your phone, you can ensure that only authorized users can access your site.
Also, read How to Enforce Two Factor Authentication for WordPress with Plugins.
Why does enabling 2FA matter for WordPress websites?
Enabling 2FA on your WordPress site can help to reduce the risk of brute-force attacks and password-cracking attempts. Even if a hacker manages to obtain your password, they won’t be able to access your account without the additional factor of authentication. WordPress supports a variety of 2FA methods, including SMS verification, email verification, and authenticator apps like Google Authenticator and Authy.
How to Enable 2FA on Your WordPress Site?
Enabling 2FA on your WordPress site is a simple process.
- First, you’ll need to install a WordPress security plugin that supports the authentication method you want to use. Some popular options include Two-Factor, Google Authenticator, and Authy.
- Once you’ve installed and activated the plugin, you can configure the settings to enable 2FA for your users.
- Once you’ve configured the settings, users will be prompted to set up 2FA when they login to their accounts.
- They’ll need to follow the steps provided by the authentication method to complete the setup process.
Implementing Security Headers

Security headers are HTTP response headers that provide additional security measures to your website by allowing your website to communicate security-related information to the user’s browser. Despite the benefits of using security headers, many website owners still don’t implement them.
How to Implement Security Headers on Your WordPress Website?
Add the following to your .htaccess file to implement security headers.
# Security Headers
Header always set Content-Security-Policy "upgrade-insecure-requests"
Header always set X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff"
Header always set X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block"
Header always set Referrer-Policy: "no-referrer-when-downgrade"
Header always set Expect-CT "max-age=7776000, enforce"
Header always set X-Frame-Options: "SAMEORIGIN"
Header always set Permissions-Policy: ""
Header always set Strict-Transport-Security: "max-age=31536000"
env=HTTPS
Adding security headers can help prevent security threats like cross-site scripting (XSS) and clickjacking, making your website more secure. To implement security headers on your WordPress site, you can use a plugin like WP Security Headers that adds the necessary headers to your website’s HTTP response or manually add the necessary headers to your website’s .htaccess file.
Additionally, use a reliable hosting provider that offers features like a free SSL certificate and a web application firewall to further enhance your site’s security. Opt for quality hosting and a dedicated IP address for added protection against attacks.
The most commonly used security headers include:
- Content Security Policy (CSP)
- Strict-Transport-Security (STS)
- X-content-type-options
- X-frame-options
- X-XSS-Protection
To Sum up
Securing your WordPress site requires a proactive approach to identifying and avoiding common WordPress security mistakes. From outdated software and weak passwords to neglecting user roles and file permissions, there are many ways that hackers can exploit vulnerabilities in your site. By implementing the best practices outlined in this article, including choosing a secure hosting provider, updating your software, using strong passwords, using features like ‘limit login attempts’, and regularly auditing your user roles and file permissions, you can significantly reduce the risk of a security breach. Improving the security of your website is crucial not just for protecting your data, but also for preserving your search engine optimization (SEO) and earning the trust of users.



Common WordPress Security Mistakes to Avoid in 2023